Exploring the Different Types of Oxygen Therapy: A Complete Guide
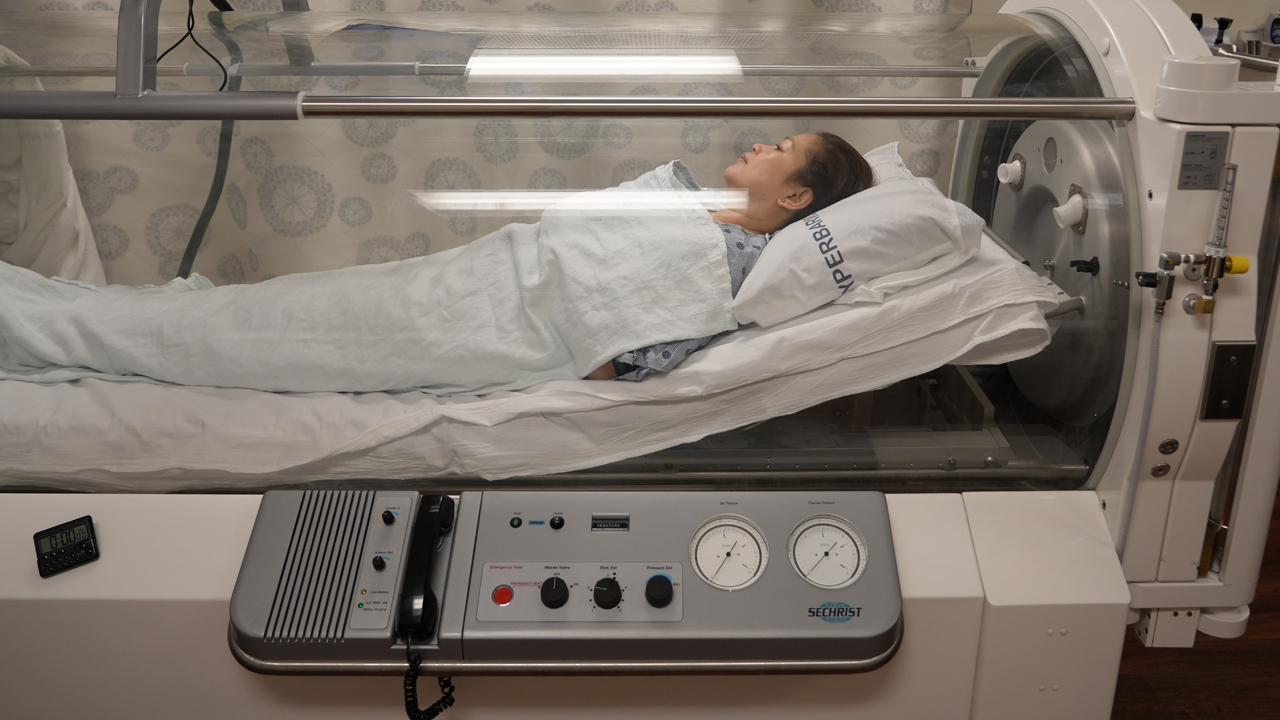

Table of Contents
ToggleOxygen therapy is a critical treatment used in many medical conditions to maintain adequate levels of oxygen in the blood and improve overall health. Whether used for chronic respiratory diseases, acute injuries, or recovery from surgery, supplemental oxygen can play a crucial role in supporting the body’s organs and tissues. This article will explore the different types of oxygen therapy, the methods of delivery, and how they are used in various clinical settings.
What is Oxygen Therapy?
Oxygen therapy is the administration of oxygen at higher-than-normal concentrations to individuals who have difficulty absorbing enough oxygen from the air due to various health conditions. Oxygen is essential for cellular function and energy production. When oxygen levels in the body drop below normal, it can lead to complications such as fatigue, organ dysfunction, or even organ failure.
People with diseases that impair lung function—such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, pneumonia, and heart failure—often benefit from oxygen therapy. By increasing the amount of oxygen available to the body, oxygen therapy helps to maintain proper organ function, reduce fatigue, and improve overall quality of life.
Different Types of Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy is not a one-size-fits-all treatment. Depending on the condition being treated, the severity of oxygen deficiency, and the patient’s specific needs, different types of oxygen therapy may be recommended. The primary methods of oxygen delivery include:
1. Nasal Cannula
A nasal cannula is one of the most common devices used for oxygen therapy. It consists of a lightweight tube that is inserted into the nostrils, delivering oxygen directly into the airways. The nasal cannula is suitable for individuals who need low to moderate levels of oxygen and who can breathe comfortably through their nose.
- How it works: The cannula is connected to an oxygen source, such as an oxygen tank or concentrator. The patient breathes in oxygen via the two prongs that rest in the nostrils.
- Advantages: It’s non-invasive, comfortable, and allows for easy speaking and eating. It’s ideal for patients who need oxygen while still being able to go about their daily activities.
- Common use: The nasal cannula is commonly used for patients with conditions like COPD, asthma, or during recovery from surgery.
2. Oxygen Mask
An oxygen mask is a larger device that fits over the nose and mouth. It provides higher concentrations of oxygen than a nasal cannula and is used when a higher flow rate of oxygen is needed.
- How it works: The oxygen mask is connected to a source of oxygen and covers the patient’s nose and mouth. Oxygen flows into the mask and is inhaled through the nose and mouth.
- Advantages: Oxygen masks can deliver higher concentrations of oxygen and are often used in emergency situations or for patients who require more oxygen support than a nasal cannula can provide.
- Common use: It’s used for patients in more critical conditions, such as those with pneumonia, respiratory failure, or severe COPD exacerbations.
3. Non-Rebreather Mask
A non-rebreather mask (NRM) is a special type of oxygen mask used in emergency situations. It allows for high concentrations of oxygen and is typically used for patients experiencing acute respiratory distress.
- How it works: The NRM features a one-way valve and a reservoir bag that fills with oxygen. As the patient inhales, oxygen from the reservoir is delivered, and exhaled air is expelled through a valve. This ensures that the patient receives the maximum amount of oxygen with minimal rebreathing of exhaled gases.
- Advantages: Provides very high concentrations of oxygen—up to 90%—and is highly effective in emergency situations.
- Common use: Non-rebreather masks are typically used in hospitals for patients with severe respiratory distress, such as those with respiratory failure, severe asthma, or carbon monoxide poisoning.
4. Venturi Mask
The Venturi mask is another type of oxygen delivery system that provides a controlled and precise flow of oxygen. It’s particularly useful for individuals who need a specific concentration of oxygen.
- How it works: The Venturi mask uses a color-coded system to regulate the flow of oxygen. By adjusting the mask’s settings, healthcare providers can ensure that the patient receives a specific oxygen concentration, typically ranging from 24% to 60%.
- Advantages: It provides precise control over the oxygen delivered, making it ideal for patients who need a steady and specific amount of oxygen.
- Common use: It’s commonly used for individuals with conditions such as COPD, where too much oxygen can lead to respiratory complications. The controlled delivery of oxygen prevents complications and maintains stable oxygen saturation levels.
5. Oxygen Concentrators
An oxygen concentrator is a machine that extracts oxygen from the surrounding air and delivers it to the patient. It’s typically used for long-term oxygen therapy at home.
- How it works: The oxygen concentrator draws in ambient air, filters out nitrogen, and compresses the oxygen to deliver a steady, reliable flow to the patient. It can be used with either a nasal cannula or an oxygen mask.
- Advantages: Oxygen concentrators are portable, convenient, and allow patients to receive oxygen continuously without the need for large, heavy oxygen tanks. They are cost-effective in the long term and suitable for home use.
- Common use: Oxygen concentrators are typically used by individuals with chronic respiratory conditions, such as COPD, who require continuous low-flow oxygen at home.
6. Portable Oxygen Tanks
Portable oxygen tanks are another option for individuals who need oxygen therapy on the go. These tanks are small, lightweight cylinders that contain compressed oxygen.
- How it works: The patient attaches a nasal cannula or mask to the tank’s regulator, which controls the flow of oxygen. The portable tank allows for mobility and can be carried during daily activities.
- Advantages: Portable oxygen tanks are highly flexible and allow patients to travel or remain active without being confined to stationary oxygen equipment.
- Common use: They are often used for people who need oxygen therapy temporarily or those who require intermittent oxygen supplementation during physical activity.
7. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a specialized treatment that involves breathing 100% oxygen in a pressurized room or chamber. This type of therapy is used for more specific medical conditions.
- How it works: The patient is placed in a pressurized chamber where they breathe in pure oxygen. The pressure increases the amount of oxygen dissolved in the blood, promoting healing and improving oxygen delivery to tissues.
- Advantages: HBOT is used to treat conditions like decompression sickness (common among divers), severe infections, wounds that won’t heal, and radiation injuries. It can significantly speed up healing and reduce inflammation.
- Common use: HBOT is primarily used in hospital settings for the treatment of deep infections, chronic wounds, and certain neurological conditions.
When is Oxygen Therapy Used?
Oxygen therapy is used for a wide variety of conditions, including:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Pneumonia
- Asthma
- Congestive Heart Failure
- Sleep Apnea
- Stroke
- Heart Attack
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
- Surgical Recovery
- High-Altitude Sickness
- Wound Healing
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for specific injuries
Conclusion
Oxygen therapy plays a vital role in managing various medical conditions that affect the body’s ability to absorb enough oxygen. By understanding the different types of oxygen therapy, their delivery methods, and their benefits, patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions on the most appropriate treatment for each individual’s needs. Whether used for long-term chronic conditions or emergency situations, oxygen therapy is an essential tool for improving health, enhancing recovery, and supporting overall well-being. If you or someone you know is considering oxygen therapy, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable option for the condition at hand.